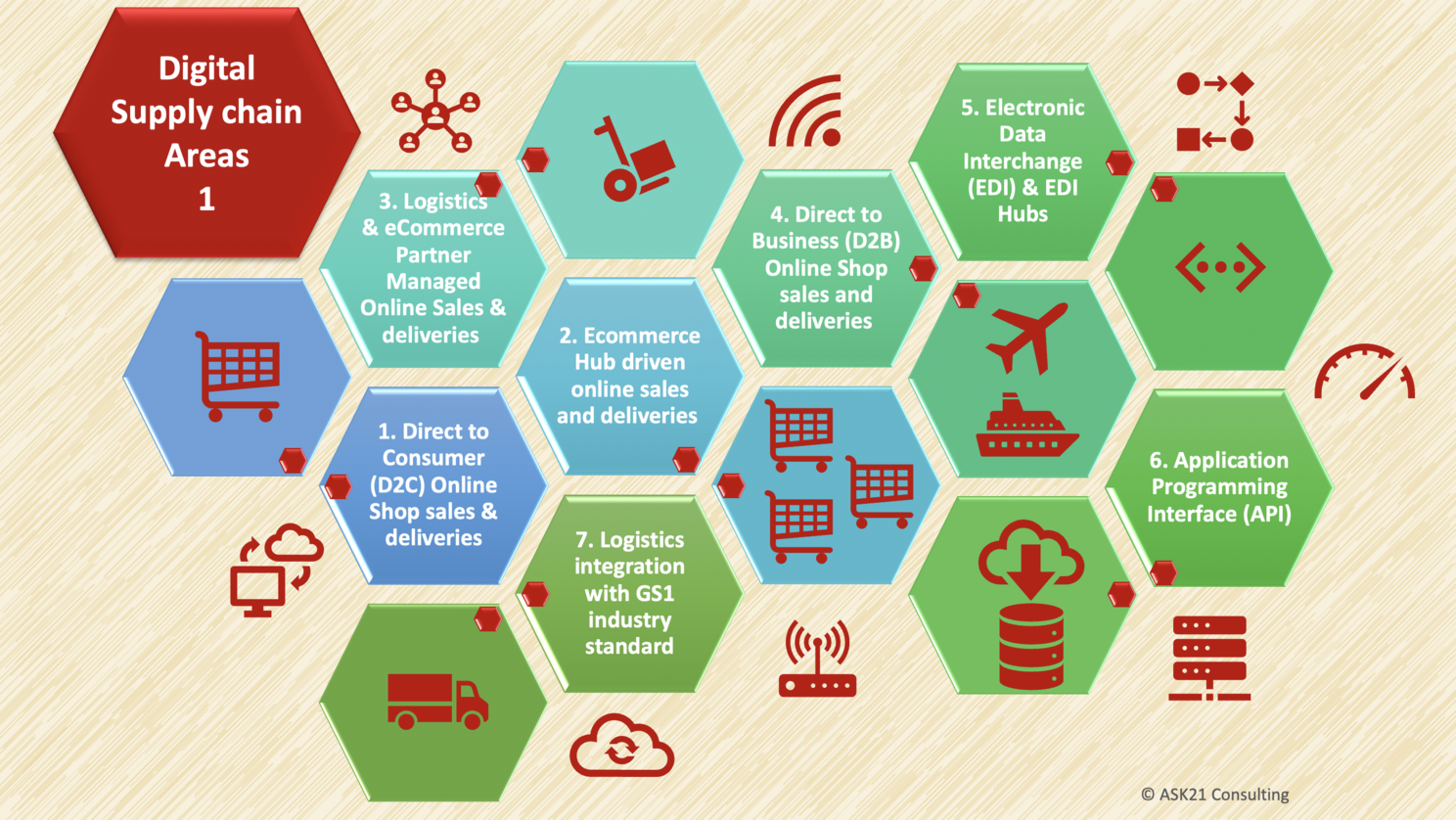
Digital Supply Chain consists of many areas of automation and digital transformation. The core is around the order to cash processes especially the above seven areas we discussed.
In addition to the seven areas discussed in the part 1 of this article, digital supply chain automation must be also done in the following supply chain areas,

1. Order to Cash (O2C) internal organization add on processes – The core Order to Cash process is normally fully automated using ERP (SAP, Oracle, Microsoft etc.) systems and integrations.
There are several add on processes that are executed outside the system. Processes related regulatory and compliance reviews and approvals, processes related to scrapping, demo product issuance and audits, processes related to warehouse clearance or slow-moving stocks clearance sale and many more.
All such processes can be automated using specific systems or simple workflows using platforms and products like Microsoft SharePoint.
Repetitive and standard tasks to be performed on day-to-day basis can be automated with robotics process automation where computers can be trained to do exact same action steps at specific time interval that is done by SCM team member.
2. Logistics Outbound processes automation – For supply chain to work seamlessly, the logistics warehouse partner’s processes must be automated and integrated. Core process are automated using warehouse management system.
There other internal processes related to pick, pack, track, deliver and report might not be fully automated. Each areas processes can be reviewed to check how much of efficiency and effectiveness can be achieved if we automate each area processes with simple workflows, robotics process automation or even standard tools from the market.
An important area is to receive proof of delivery from the last mile delivery partner in the delivery process. This can be fully automated and synched with OCR and Onscreen signature solutions to tag and monitor exact throughput time for deliveries.
In addition, the palates and packages can be marked with smart tags and bar codes to ensure exact location of palate and package can be tracked online in the system.
3. Logistics Inbound processes automation – In the Demand and Supply cycles inbound deliveries are important where the product is shipped out from factory to the shipping partner, from shipping partner to warehouse or direct to the customer). Core processes are automated using warehouse management and shipment tracking system of the shipping company.
There are several other inbound processes related to customs clearance, import duties, quality checks, bonded and non-bonded goods segregation storage and checks, container loads to ensure full container loads are done to efficient costs as well as shipments that are flown in through cargo planes instead of sea shipments.
In addition, the palates and packages can be marked with smart tags and bar codes to ensure exact location of palate and package can be tracked online in the system.
4. Industry and Logistics Warehouse automation – This covers the industry warehouse as well as logistics partner warehouse including bonded and non-bonded warehouse locations. The focus is on using robotics and IoT (Internet of Things) devices, tags and scanners to make it efficient to store the goods as well as locate them for picking, packing and shipping. The automation in this area improves efficiency and involves physical (hardware) as well as process (software) automation using industry 4.0 components, solutions and services.
5. Supplier integration and automation – This area focuses on industry suppliers that supply raw materials, semi-finished goods or accessories for the main product creation, packaging and shipping. The area can also include suppliers from the logistics partner side that supply raw materials to do repackaging or additional accessory addition (like power supply cords) before shipping the product out to customers and consumers.
Supplier integration can be done using APIs and EDIs for tight integration or simple upload and download of data to and from the systems by using robotics process automation.
Supplier automation can be done by looking at the processes involved and automating those with workflows or robotics process automation or systems whatever best fits the business needs.
6. Customer Service automation – An important and often disintegrated part of the supply chain is its customer service automation and integration. Customer services is in two areas, one meant for customers (distributors, retailers, online partners) and other meant for consumers (people that actually use the product or the service). Both are important and both need attention especially in the online world to ensure they are sufficiently supported and satisfied with organizations products, solutions and services.
Customer service automation for customers (distributors, retailers, online partners) is managed using online contact centers with several standard services handled through voice enabled chatbot and remaining through customer services human agent.
Automation of phone based and online survey to gather feedback from customers is also common.
In addition, support services on D2B (direct to business) and EDI (electronic data interchange) services can be also automated using chatbots to handle enquiries and get the tickets registered.
Customer service automation for consumers (people that actually use the product or the service)is managed using online customer service call centers with standard services handled through online chatbots and voice enabled chatbot. Areas that can’t be handled by chatbots are routed to consumer support human service agents from call centers.
Consumer’s customer service is largely managed using online tools like chatbots, ticket logging and online search assistants that assist in finding the information needed by the consumer.
Consumer service support surveys are full automated using phone based, sms based and web-based survey tools.
In addition, there are also consumer service support from the online partner platforms from where the consumer purchased the product. These areas are also automated using similar solutions and platforms.
Post purchase product warranty registrations and support are also part of the consumer services. These are automated using online web platforms where consumers can register their purchases.
The appointment bookings for the customer service for returns, cancellations, replacements and repairs walk ins can be neatly organized to avoid and reduce waiting times for the customer.
7. Big Data, Monitoring and Reporting – Across the entire supply value chain, the data related to products, product movements, online transactions, offline transactions, surveys, support tickets, customs, logistics, deliveries, returns, cancellations, promotions, warranty and post purchase support etc.
Each customer, consumer and their orders result in lots of customer/consumer touch points across the entire value chain where each interaction data is collected and stores in respective systems. Not just organization’s systems but also suppliers, online business partners, logistics partner and delivery partner systems.
All this data has tons of useful insights and patterns which can help the organization and its partners to improve their efficiency, effectiveness, sales and services.
All such data can be structurally translated to data cubes and stored in data lakes. The data lakes can be connected to various visualization dashboards that can share insights for each customer, segments of customer, product segments and even functional segments.
The slice and dice of data can be done in many forms and shapes. The organization’s need a real time or near real time (lag of few hours) online dashboards that can be used to check and make decisions with speed.
Digital Supply Chain Benefits
Digital supply chain initiatives can be part of Digital Transformation of the organization and it takes multiple months to multiple years for making the entire supply value chain digitalized.
Why must organizations embark on Digital Supply Chain initiatives? Here are the key benefits that drive the organizations towards digital supply chain,
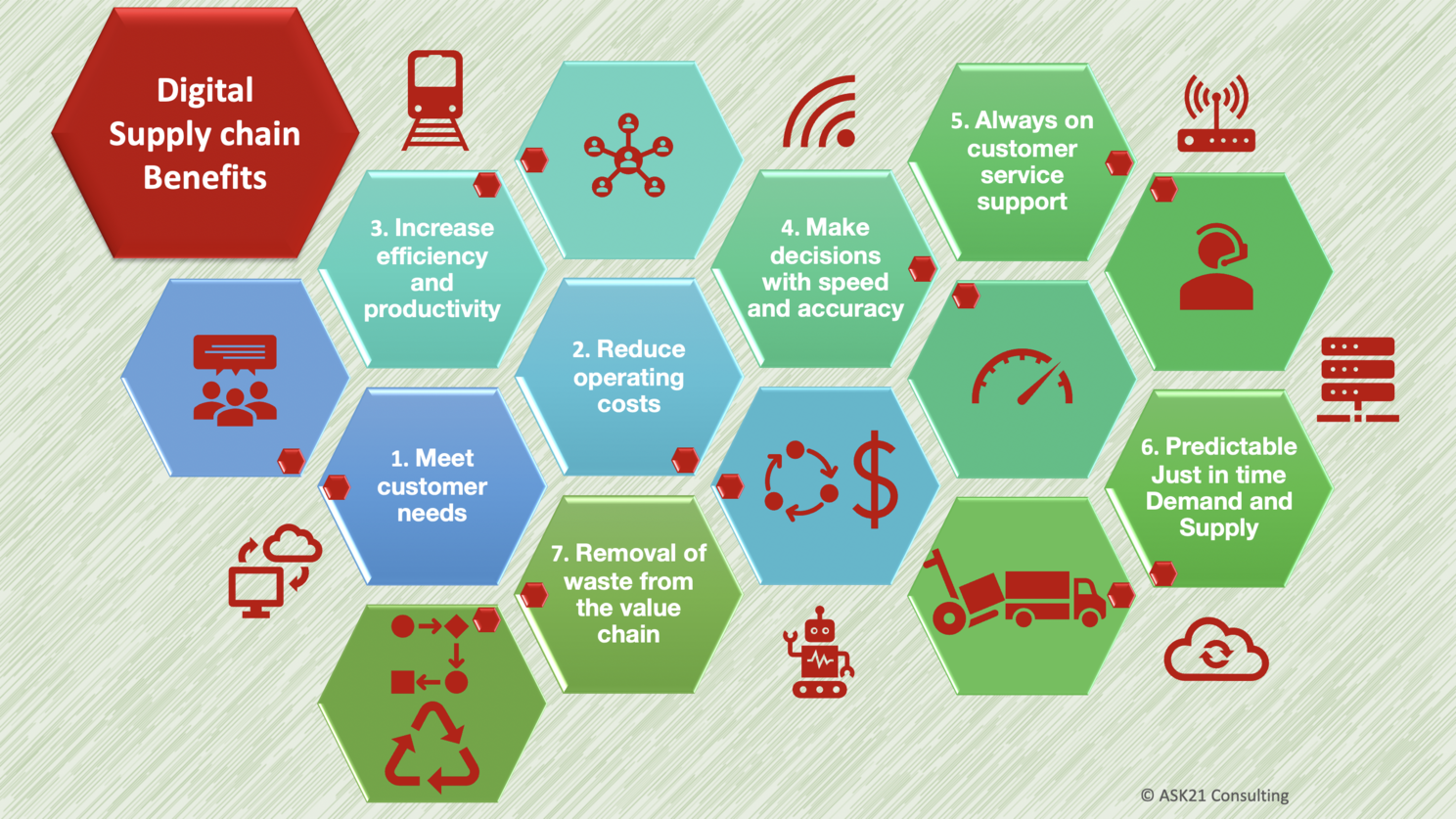
1. Meet customer needs – Digital supply chain helps organizations meet their customers’ needs as most customers prefer purchasing online and delivery done at their door steps with speed and quality. This is possible only if the entire value chain is connected and digitalized with solutions, systems, interfaces, sensors, scanners and devices.
2. Reduce operating costs – Digital supply chain ensures reduction in costs as a lot of costs of handling deliveries back and forth, carrying stocks for longer than needed, customer satisfaction and support issues etc. are reduced with structurally planned and connected value streams that are always on and working round the clock.
3. Increase efficiency and productivity – Digital supply chain help ensure the efficiency and productivity of entire supply value chain goes up including partners. This happens because repetitive tasks and non-value-added tasks are removed or automated with robotics process automation. In the warehouse it becomes easier to store and locate products using online systems and robotics that can track and bring the products to ease up picking, packing and shipping.
4. Make decisions with speed and accuracy – Digital supply chain gives an edge to the organization by bringing the insights and visualizations from the data at their fingertips. This allows them to make accurate decisions with speed to ensure they can cut down costs, improve sales and deliveries which in turn results in positive customer experience.
5. Always on customer service support – Digital supply chain enables the organization with an always on customer service that can be designed to handle queries and support customers on its own using chatbots and voice enabled call flows. It can collect all the information and route it to customer service team to step in and support. As the general and standard enquiry gets automated the customer service agents can give quality time in delivering great experience and support for the customers and consumer alike.
6. Predictable Just in time Demand and Supply – Digital supply chain enables the organization to adapt to predictable just in time demand and supply plans ensuring customer demands are met on time while the stocks don’t need to remain in the warehouse for too long incurring storage costs
7. Removal of waste from the value chain – Digital supply chain transformation means the organization will have to undergo full value stream mapping and restructuring or engineering of the value chain to identify and eliminate waste across all processes. This gives a competitive edge to the organization to have faster turnaround at lighting speed to meet the customer needs with speed. The elimination of waste doesn’t just happen in the organization but also all of its partners and suppliers as they will need to adapt to similar standards to keep the entire process seamless.
Digital supply chain 4.0 in conjunction with industry 4.0 is still in process of being deployed and improved by many organizations while top organizations might have already achieved the needful digital transformations and are now continuing improvements.
Digital supply chain 5.0 is on the horizon as we move towards Web 3.0 and 5G lightning internet speeds making everything connected, always on and seamlessly reachable across the globe. Digital supply chain 5.0 will bring hyper automation and autonomous warehouse management and even autonomous deliveries. Robotics, Robots, Artificial Intelligence and Autonomous vehicles will change the way supply chain is managed and customers are served.