Kaizen is a Japanese word with meaning “change better” or “continuous improvement”. It is method used for continuously improving business processes and value chains through small meaningful increments which over a period of time result in big improvements across the entire value chain.
Kaizen focuses on eliminating seven types of lean wastes in the value chain. Kaizen was used for almost a century by manufacturing plants of Toyota. In the past 2 decades the usage and adoption has gone up across all business industry and sectors. The Kaizen process and workflow is fully digitized with online tools and workflows (E.g., Microsoft SharePoint Workflow).
Kaizens are also referred as following,
1. Point Kaizen – The most commonly used kaizens are referred as point kaizen. These small improvements and doesn’t need a lot of efforts to implement while still having measurable impact.
2. System Kaizen – As the name suggests, it relates to improvements brought to life using IT system. The second most used kaizens are system kaizens which are widely used by most of the organizations.
3. Plane Kaizen – This is the 3rd most used Kaizen which is related to the improvements made to value stream or value chain.
Kaizen Types
If we come to discussing the types of Kaizens then there are actually five types of Kaizen methodologies, keeping in mind Kaizen means improvement (change for better) so its not necessarily small changes only but they can be large ones too:
1. Kaizen Teian – In this type of Kaizen the improvements are done bottom up instead of top down. It means improvements start at the lowest level in the organization. For this to work the Lean management mindset (continuous improvement culture) must be already well deployed across the organization. Everyone in the organizations participates and submits their improvements to improve their work, when this is done across the entire organization, it leads to large improvement in removal of lean waste. Kaizen Teian can be called as Point Kaizen as well.
2. Kaizen Events – Kaizen events are big and planned improvements in the value chain. These improvements are done by calling for a workshop with participants from the value stream planned for improvement. Participants work through VSM (value stream mapping) workshop to identify and prepare the plan to eliminate lean wastes. Kaizen events help improve the value chain significantly by improving efficiency, effectiveness and creating superior value for the customer.
3. Kaikaku – Kaikaku is a radical change and it focuses on business transformation through radical changes to its value stream and value chain. It is not so much about identifying lean waste and eliminating it, instead this is about changing the entire process of how the organization does the business. It requires significant planning and focused efforts to achieve it successfully. Digital Transformation can be one of the examples of Kaikaku.
For Kaikaku’s success, these 10 commandments can be used,
i. Throw out the traditional concept of manufacturing methods.
ii. Think of how the new method will work; not how it won’t work.
iii. Don’t accept excuses.
iv. Totally deny the status quo, be ready to start new.
v. Don’t seek perfection. A 50% implementation rate is fine as long as it is done on the spot.
vi. Correct mistakes the moment they are found.
vii. Problems give you a chance to use your brains.
viii. Ask “why” five times.
ix. Ideas from ten people are better than one person’s knowledge.
x. Kaikaku knows no limits.
Post successful implementation of Kaikaku, continuous improvements cycle can start using Kaizen.
4. Kakushin – Kakushin is break through innovation Kaizen. Kakushin is related to switching over the entirely new way of working in the value chain. It’s related to breakthrough innovation in how the organization functions in its value stream. It is entirely changing (not transforming) the value stream of the organization. E.g., switching production line from manual or semi-manual to a production line entirely managed by robotics and robots. Kakushin requires large risk taking to transform how an organization functions and does its business (E.g., We can say that apple has undergone Kakushin. Same can be said about Tesla cars manufacturing etc.)
5. Kaizen Blitz – Kaizen Blitz are similar to Kaizen events but in smaller scale. Kaizen blitz are achieved by calling for small workshop of few hours to a day max to identify improvements. These improvements are then immediately taken up and deployed with in 3 to 5 days. Improvements are chosen in way that they can be done quickly with speed and deliver huge improvement.
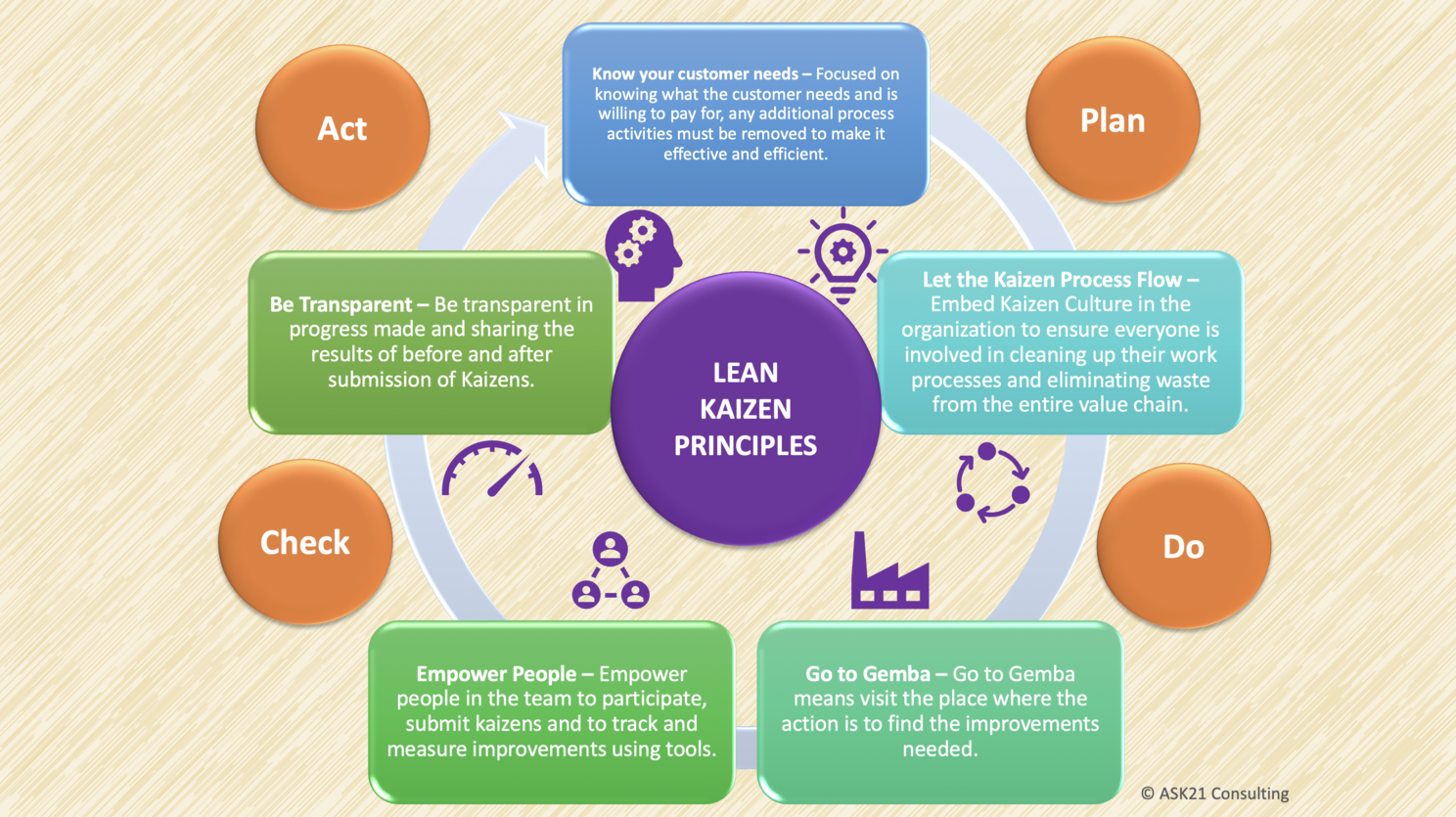
Kaizen Principles
There are 5 Kaizen Principles that make the Kaizens efficient and effective. The 5 principles are:
1. Know your customer needs – Focused on knowing what the customer needs and is willing to pay for, any additional process activities must be removed to make it effective and efficient.
2. Let the Kaizen Process Flow – Embed Kaizen Culture in the organization to ensure everyone is involved in cleaning up their work processes and eliminating waste from the entire value chain.
3. Go to Gemba – Go to Gemba means visit the place where the action is to find the improvements needed.
4. Empower People – Empower people in the team to participate, submit kaizens and to track and measure improvements using tools.
5. Be Transparent – Be transparent in progress made and sharing the results of before and after submission of Kaizens.
Kaizen Process Flow
Kaizens can be managed using the following simple process steps,
1. Identify the process and area of improvement
2. Analyze the process and its current performance
3. Identify & document wastes (gaps)
4. Identify & document improvements
5. Complete Kaizen plan, review and approvals for execution
6. Execute and Test Kaizen Changes
7. Implement tested improvement changes
8. Measure results and report current vs new performance gains
9. Mark the Kaizen as completed
10. Maintain continuous improvement

Kaizen Tools (Methods and Approaches)
For making Kaizens more effective and efficient several effective methodologies and approaches must be applied. Here are the methods and approaches that can be used,
i. The 5 W + H Model – Use 5 the Why model (Who, What, Where, When, Why and How) for identifying the root cause, gaps and improvements.
ii. Lean Wastes – Use TIMWOOD (Transportation, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Over production, Over processing and Defects) waste identification to identify waste types and related improvements.
iii. The Deming Cycle – Use Deming’s PDCA (Plan Do Check Act) cycle for the effective execution of Kaizens.
iv. The 5 S Framework – Use the Lean 5S framework (Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu, Shitsuke).
· Seiri (Sort) – Sort only what is needed where is needed.
· Seiton (Simplify) – A place for everything and everything in its place.
· Seiso (Sweep) – Clean the workspace and keep it clean.
· Seiketsu (Standardize) – Standardize the first three “S.”
· Shitsuke (Sustain) – Stick to the first 4S.
v. Ishikawa Method – Use the Ishikawa method of applying 5M’s (machine, method, material, man/mind power, and measurement/medium)
vi. Lean Management 6P Method – Use the 6P method (Policy, Process, People, Plant, Program & Product) of Lean Management
vii. Kanban Visualization Board – Use Kanban board for kaizen implementation actions tracking and monitoring.
Kaizen Template
A standard Kaizen template is useful for effective documentation and reviews. Here is simple sample template overview,

Kaizen Benefits
Kaizen culture and improvements have many benefits for the organization. Here is a quick overview of benefits,
i. Elimination of waste in the value chain
ii. Improved effectiveness and efficiency
iii. Productivity gain across the organization
iv. Sharing and use of best practices
v. Costs reduction due to elimination of waste
vi. Improved quality of outcomes and outputs
vii. Improved customer experience
viii. Better value creation for the customer
ix. Improved teamwork and employee engagement
Once the whole organization starts to think about eliminating waste at their levels and finding better ways to do things, their productivity goes up significantly, quality of products/solutions/services increase, value creation for customer gets better, costs reduce and employee engagement goes up.
Kaizen is more of culture & mindset than just a framework or tool of Lean Management. Kaizen works well and result in massive improvements across the organization’s value chain delivering superior value to the customer.