Kanban system was created by Taiichi Ohno from Toyota. The purpose was to have a card system for Just in time (JIT) lean manufacturing on the product floor. The idea originated to ensure short cycles of production based on actual demand with speed and accuracy.
It involved ensuring the factories spare parts (from suppliers) and finished goods (on the shop floor and warehouse) are just in time received and processed based on actual demand. This reduced the need for stocking of parts as well as finished goods by the manufacturing units. It also reduced all the resources costs to manage all the unwanted additional resources.
The Kanban system was made in such a way that at each stage of the production line the inventory is maintained as per the capacity limits. Any ups and downs are reported and addressed to ensure the end-to-end system remains smooth. The whole system worked based on bins and card system. The bin consisted of parts and the cards represented the number of parts requested at what time at which point etc.
Kanban prescribes a strict set of rules to be adhered to ensure it functioned well. The rules were as per below,
1. Every process must create request (Kanban) to its suppliers only when it has used all its existing supplies.
2. Quality and Sequence of incoming requests takes precedence and production is strictly followed based on incoming requests.
3. Without a formal request, no shipments and transports are allowed.
4. The items transported must have the request cards attached to ensure full transparency.
5. Quality is of utmost importance so no defective parts should be sent as they will impact the production and finished goods.
6. If there are pending requests above the threshold limit setup for the production line then those would need to be addressed on priority as they will impact production throughput.
Over the past decade the entire Kanban systems of cards and bins have been computerised by all manufacturing plants worldwide. In many ways the manufacturing Kanban systems are also integrated to enterprise resource planning systems (ERP). The computerised Kanban systems use messages, bar codes, scanners, emails and systems.
In the electronics Kanban system the bins interact with each other through the electronic cards specifying the parts, the inventory quantity, time slot and stage etc. There are two type of Kanban systems in the manufacturing plant,
Production Kanban: The production Kanban produces a fixed amount of parts or products as per the requests received and the parts are placed the requested bin consisting the Kanban request.
Transportation Kanban: The transportation Kanban as the names suggested related to the transportation of the requested parts. It is used to ensure full container loads are transported to the requested production workstations.
In the past 7 to 8 years the Kanban framework for Agile product, project, program and portfolio management has been introduced and is used by several organizations worldwide.
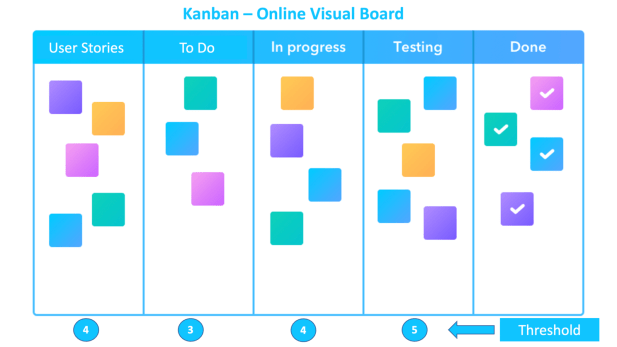
The Agile Kanban Framework works with visual dashboards consisting of Agile stages and progress update. Each stage also has a threshold which when crossed, requires attention and resolution to avoid it becoming a bottleneck. The steps can be defined as follows,

1. We can consider the visual board as a workflow consisting of electronics cards (look like post it notes).
2. The cards are actually user stories that need to be developed, tested and delivered.
3. The stages and stage names can be altered as per the product, project or program team needs.
4. Each stage (E.g. User Stories, To Do, In Progress, Testing and Done) has its own threshold based on the upper capacity of that stage resources. The stages can be also taken as columns in the swim lane of workflow (flow of work/cards).
5. The cards are moved from one stage to the next by the respective team member or owner of the Kanban board.
6. The board helps to visualize progress of various stories as well as track any bottlenecks requiring attention (e.g., in the Testing stage if there are more cards waiting then the Threshold, then it points the attention to resolve any issues faced to speed up testing)
7. Threshold is nothing but maximum amount of work the respective stage team can manage. So if a stage says 5, it means the maximum number of cards (user stories or tasks) the team can manage is 5 and anything beyond that would become a bottleneck.
8. If more than one stage crosses their maximum threshold then the work is stopped and all attention is given to the two stages to clear the bottleneck and backlog.
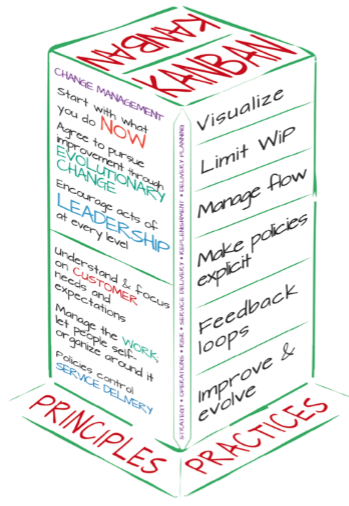
Here is a glance overview of Kanban principles and practices prescribed by Kanban university,
Kanban for Agile project management is more simpler than Scrum or any other Agile framework. This is because it works with a simple visual dashboard and requires no stipulated roles. The team decides how many stages and what roles they will need to operate the dashboard. Kanban is considered a continuous process and so it is not bound by project management principles. Instead it works on its principles of workflow with push and pull mechanism to move tasks across the board to completion.
This makes the Kanban approach effective but more relaxed and open ended while for agile there is timebox approach and speed are necessary. So to make Kanban based agile product, project and program management more effective and efficient, a hybrid approach is used by many organizations.
One such hybrid approach is called Scrumban which is mixture of Agile Scrum and Kanban Frameworks. The combination improves the efficiency of both the models. Scrumban consists of Scrum User stories, Sprint planning, Sprint reviews, along with Kanban principles of visual dashboard for progress tracking, push – pull mechanism to move tasks, work in progress threshold limits and just in time availability.
It also helps tighten the loose end on time using timebox approach. Scrumban removes all Scrum roles and follows Kanban principle of every one is considered to be at same level in the team.
Here is a quick overview showing comparison of Scrum, Kanban and Scrumban Frameworks.

In a similar manner, scaled agile framework (SAFE) has Kanban applied to its portfolio, program and project management stages to improve its efficiency, flexibility and visibility of progress across the enterprise.
Kanban agile project management can be electronically achieved with ease using solutions and application platforms like Jira, Trello, Monday and Kanban flow. Jira and Trello are the best platforms for online agile project management.
Kanban is widely recognised and started two to three decades back for Lean JIT (Just in time) Manufacturing. The adoption of Kanban for Agile project management is easier as many organizations already use it for their manufacturing sites. The Hybrid approach of combining Agile and Kanban Frameworks allows new opportunities for more flexibility and scalability in product, project and program deliveries.