Deepfakes have emerged strongly only in the past few years. The name comes from Deep (Deep Learning) and Fakes (virtual, imaginary computer visuals). Deepfakes are an existing image or video created using artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and deep learning techniques by the computer system that can mimic to look & feel 98% similar to our actual image and videos.
Deepfakes are created using AI and ML to create visual and audio content that can easily deceive people. The key technology and learning methods used come from deep learning and involve use of generative neural network architecture for training machine and generating output. It uses autoencoders, decoders and generative adversarial networks (GANs) from deep learning.
Here is a brief overview of the Deepfakes are created and operated,
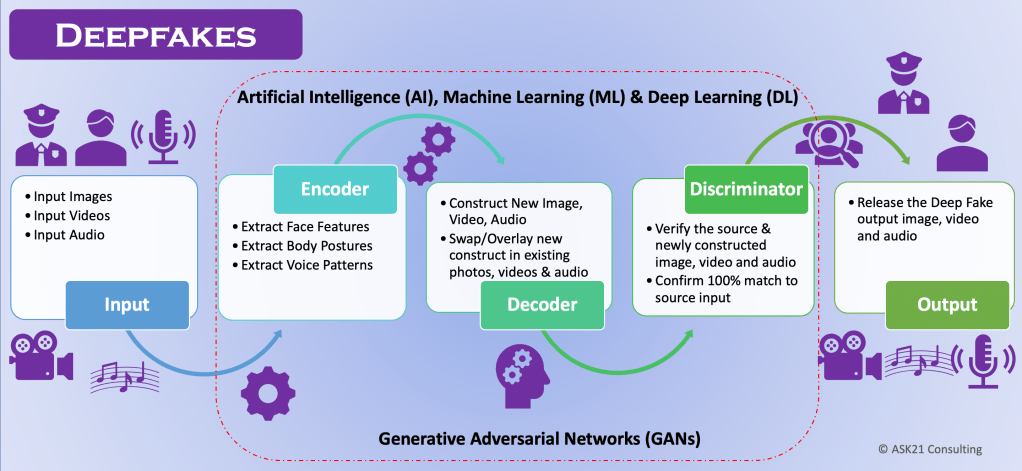
1. Deepfakes work based on an autoencoder which is part of neural network in deep learning architecture.
2. The autoencoder reduces a person’s image to a low dimensional latent space.
3. The latent space captures the key features of person’s face and body postures etc.
4. This is then used by the decoder to reconstruct the image from its latent representations.
5. The decoder works as part of generative adversarial network (GAN). The GAN trains the output generator consisting of the decoder and discriminator.
6. The generator constructs the image from the latest representation while the discriminator checks and determines if the image constructed is matching to the source.
7. The model then places the reconstructed image and features on top of the person’s video or image to mimic like the real person itself.
8. As the entire architecture is functioning with AI, ML and Deep learning the model continues to take feedback, learn and evolve and it becomes so perfect that it’s almost impossible to differentiate between original source and deepfake reconstruct.
Now that we understand how deepfakes are created and operated, let’s understand why they are worse than good for society and organizations.
Deepfakes are not just be used on image and videos but also for mimicking audio. Deepfakes are not just be used for one person but even the entire group of people can be mimicked in an image, audio and visual. This is what makes them very dangerous as we can’t easily interpret fake Vs real on our electronic devices.
Deepfakes are generally used for mimicking others. They are often used by bad people targeting celebrities and leaders. The internet is full of bad examples of deepfakes. Some are even so shameful that we can’t even imagine.
There are some good sides of Deepfakes too. On the good end deepfakes can be used for,
1. Reviving memories of people who have left the world and bringing them to life with virtual images and videos of them.
2. Reviving memories of patients with short memory and memory loss.
3. Marketing and Creative agencies are using deepfake to save time and costs on advertisements where the celebrity can shoot the ad just once and the audio content of the ad can then be mimicked and targeted towards respective target audience in their language making it more personalized and effective.
E.g., one such ad was from the leading food delivery company that is targeting its customers in different states and cities in different language using the Deepfake technology. The Deepfake celebrity is mimicked so clearly and accurately that the viewers can’t make out any difference and ad became very personalized and highly successful.
4. Mobile Phone and website based apps for online learning of concepts by mimicking the actual creators of those concepts.
E.g., Einstein teaching his theories to school and college students using online learning videos.
Deepfakes require strong internet connections and generally with weaker connection the lag can easily show up that the video is fake. But as the technology improves and countries move from 4G to 5G as well as the AI platforms and solutions becoming stronger along with Metaverse possibilities, it can lead to serious problems for many areas.
The solution to protect ourselves from bad sides of Deepfakes is to be careful,
1. Using your photos, voice and videos on social media and storage platforms openly.
2. We must ensure everything is well encrypted and securely stored.
3. Always be vigilant in day-to-day life and be alert and aware while using internet.
4. Stay away from using open (unsecured) and free access wireless network points.
5. Ensure you always use strong password on all your devices and change it periodically this will ensure your devices and accounts are always secured.
6. Stay away from mobile apps and websites offering Deepfake free trial or even paid trials.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL) and many other new technologies have many benefits for organizations, society and people. But its very important to have a solid and secured good governance on how these new technologies can be used for the greater good of all.