In the previous article you have seen why use lean problem solving, what are the types of problem solving and some examples. In this article let’s understand the process of Lean Problem Solving.
Once you have identified the type of problem faced in the value stream or value chain, they next step is to understand how to structurally work on detailing, analyzing, find the root cause, implementing resolution and monitoring it to ensure the value stream or value chain works as per expected.
By removing the obstacles the organization continues it trajectory of becoming better at delivering customer value and eliminating waste across the entire value chain.
For effectively solving the problem, lean management prescribes an eight step structured process to be followed. The steps can be , there are The steps in the Lean problem-solving process are as follows:
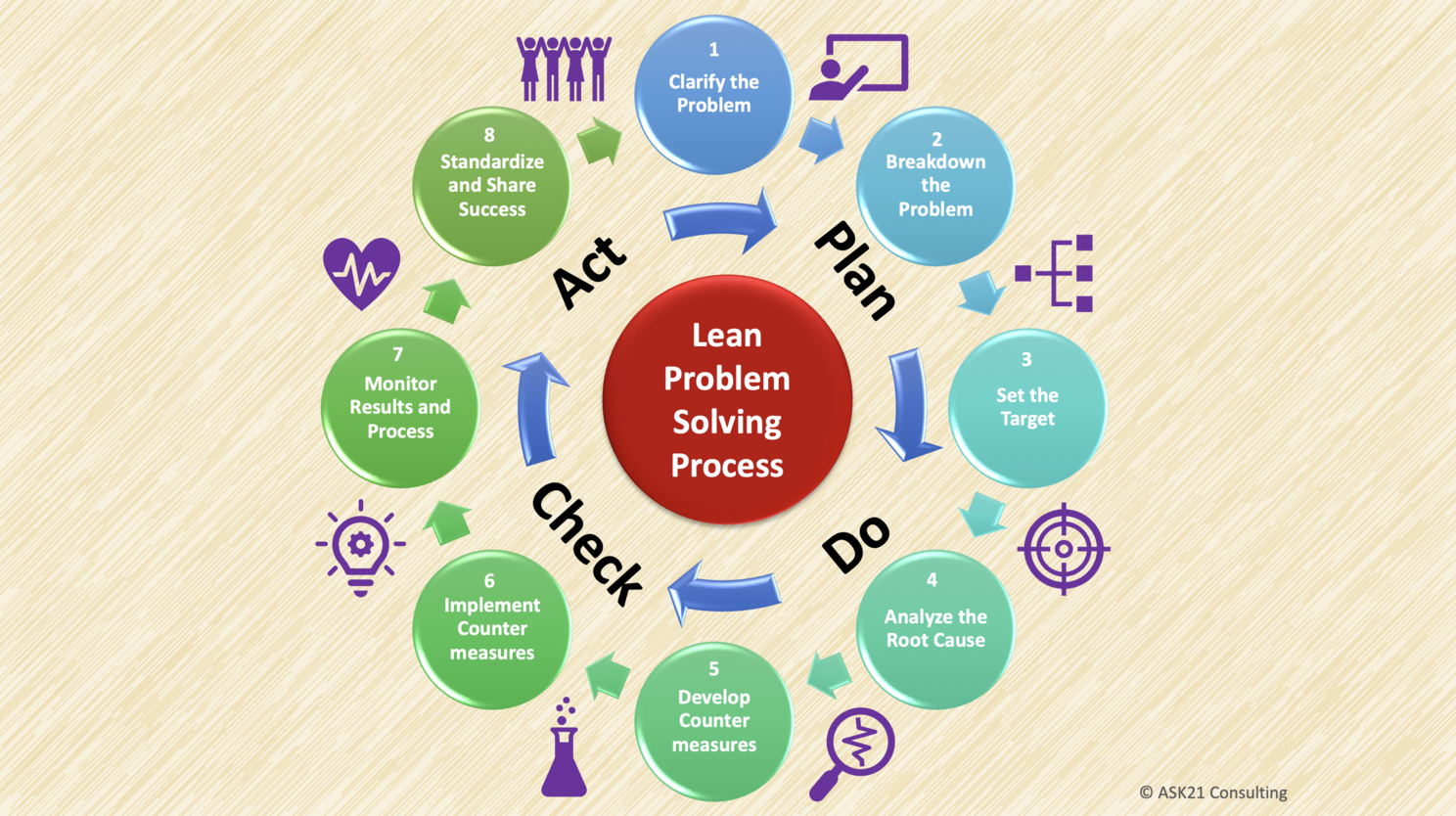
1. Clarify the Problem – In this step the team needs to go to gemba and identify the type of problem as well as do necessary clarifications to ensure the problem is clearly articulated and understood by all in the same way. Always keep in mind that different people will see the same problem differently and this is why this step is critical in ensuring everyone see the problem correctly.
2. Breakdown the Problem – The easiest way to solve the problem is to break it down in smaller pieces and then analyze each piece with respective team members to understand the cause and effects clearly. During the earlier step different set of areas might have been reported related to same problem. Breaking down the problem in to smaller areas or smaller pieces makes it easier to go through each with the right focus and tools.
3. Set the Target – Based on the type problem, it is important to set a realistic target to get it resolved with speed and accuracy. The target must be established keeping in mind the impact of the problem on the entire value chain and how fast it needs to be addressed to remove the blockage. It is also equally important to understand capacity and capability of the team in resolving the problem. People with right expertise and experience must be involved to set the target and resolve the problem.
4. Analyze the Root Cause – This is an important step in problem solving where the root cause analyses needs to be performed. The root cause analyses can be performed using fishbone diagram and 5 Whys method. There can be other tools and techniques also applied like the Problem Tree method to clearly articulate the core problem, it’s possible root causes and impact or effect of those. This needs to be done with the team to ensure all inputs are correctly captured and documented.
5. Develop Countermeasures – After the root cause analysis is completed, the team can focus on identifying and developing counter measure to remove the obstacles and resolve the problem. The focus should be on having counter measures for each root cause or even better one countermeasure that can address and resolve multiple root causes. It is important that the effect of counter measure must be thought through as well to ensure they do not create more impacts and/or gaps in the value chain outputs.
6. Implement Countermeasures – One of the important steps in the problem solving process is to test and implement the counter measures. Before implementing it, the counter measures must be tested and validated with a possible dry run to ensure they will work as per planned and not create any new impact to the value chain. Upon successfully testing and validation the counter measures can be implemented as per planned schedule.
7. Monitor Results and Process – Post implementation close monitoring and reporting must be enabled for capturing the results from the value chain and especially the impacted area. The entire value chain process must be kept under monitoring to confirm that the before and after implementation of countermeasures have standardized the output results.
8. Standardize and Share Success – After a pre-defined period of monitoring and reporting, the problem can be marked as fully resolved and completed. At this stage the standardised process can be replicated across in case there are more similar instances of the process running (E.g., an application with multiple instances). The success can be also shared widely in the organization to ensure everyone is kept informed about the problem and how it was resolved.
Along the entire problem solving process there is an underlying Deming’s Cycle (PDCA) in work. Deming’s cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) helps in ensuring continuous improvement is on everyone’s mind. Here’s a quick overview of Deming Cycle stages,

1. Plan: Plan focuses on identifying, articulating and planning improvement. If we look at it from the problem solving process steps, Clarify the Problem, Breakdown the problem and Set the Target are part of Plan stage.
2. Do: Do is also about executing the change or improvement. We can also relate it to Design, Build and Test and Implement parts. If we look at it from the problem solving process steps, Analyze the root cause, Develop Countermeasures and Implement Countermeasure are part of Do Stage.
3. Check: Check comes after implementing the improvement to monitor and report results. Check is all about monitoring and reporting to confirm that the improvement, change or problem solving is working fine across the value chain. If we look at it from the problem solving process steps, Monitor results and Process step is part of Check stage.
4. Act: Act is focused on making the change or improvement stick and making it a best practice by adhering it across the organization. If we look at it from the problem solving process steps, Standardize and Share Success step is part of Act stage.
The PDCA cycle continues as the improvements are never over. For the problem solving part also the problem is resolved but further improvements and standardization as well as raising the standard to the next level continues.
Lean Problem Solving is important for all organizations. It helps to remove the obstacles in the value chain / value stream and brings the organization to the new standard, reducing costs, improving efficiency, effectiveness, and value for the customer.
